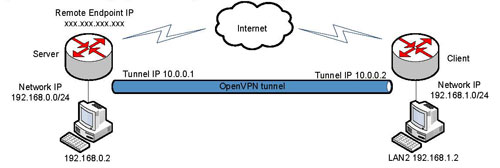
The exchange of information between different locations is a deeply felt requirement and today it is extremely easy to achieve this at an affordable cost by implementing a VPN. A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a type of interconnection between computers that allows, in a logical way, to understand in a LAN (Local Area Network) computers residing in any part of the planet. Usually we consider a LAN as a network of local computers, identified by an IP address and class (eg: 192.168.0.0 / 24, 10.0.0.0 / 24 etc.). With a VPN connection, a computer that is physically outside of that LAN can be a perfect member.
In other words, we will have to create a channel or virtual tunnel that connects two networks, in the simplest case represented by two computers reachable via the Internet. Obviously, this system must guarantee a high degree of safety. Access must be allowed only to authorized users, data in transit on the public network must be encrypted in order to prevent the risk of data theft and alteration of the information transmitted.
In our case we analyze the possibility of creating a VPN network between wireless devices, thus allowing to integrate devices distributed over a geographical network and connected to the wireless telephone network as if they belonged to the same physical LAN network. In this way a network of geographically distributed remote devices such as cameras, RTU systems, etc. can be reached directly with their IP address as if they were physically connected to our LAN. THE WLink cellular routers the OpenVPN protocol is available on our site, which allows you to create an encrypted and protected communication tunnel on the Internet.
OpenVPN is a VPN program written by James Yonan and released under the GPL, it is used to create point-to-point encrypted tunnels between computers. It allows hosts to authenticate with each other by means of shared private keys, digital certificates or user / password credentials, is available for free for both Linux operating systems and Windows GUIs.
Two hints on the implementation, among the different possible authentication systems we choose to use the static key one which allows to have a good compromise between the communication security and the implementation simplicity. On the server side we use a PC with the OpenVPN program installed, while for the client side we use the router, of course the PC must be connected to the Internet and have a static IP address (If equipment such as routers are interposed between the PC and the Internet network and firewall it will be necessary to provide for the correct routing of data). The first step is to create the key to be used on the two points of the VPN, it is possible to generate the key using a PC or directly from the configuration web page in the RUT105 router.
On PC running from command line openvpn --genkey --secret static.key, a text file will be generated static.key, which contains the key to be installed both on the server side and on the client side. On the server side, the file will usually be copied to the configuration directory of the program C: \ Program Files \ OpenVPN \ config. While on the client side it will be copied to the router following the information given in the manuals. In the download section you can download a simple Mini How-to guide that explains how to configure two PCs, one as a server and one as a client to create a VPN between the two. This solution can be useful for testing the connection before implementing it on the router.