We all have magnetic cards in our wallets, from ATM cards to corporate ID cards. And company cards are used to manage utilities within the company, such as opening doors, usability of meals in the canteen, etc. In this note we report a project for reading magnetic cards.
 The magnetic cards or badges or in English Magnetic Stripe Card are PVC plastic cards in which a magnetic strip is applied on one side. We can consider the latter as a piece of tape in an audio cassette, which is therefore suitable to contain information non-volatile. They can be read using a simple sliding reader such as the one visible on the side. The reader used is a reader with RS232 serial output able to read all the traces of the paper, so it is suitable for any type of application.
The magnetic cards or badges or in English Magnetic Stripe Card are PVC plastic cards in which a magnetic strip is applied on one side. We can consider the latter as a piece of tape in an audio cassette, which is therefore suitable to contain information non-volatile. They can be read using a simple sliding reader such as the one visible on the side. The reader used is a reader with RS232 serial output able to read all the traces of the paper, so it is suitable for any type of application.
The standard that defines the characteristics of the magnetic cards is the ISO 7810 for the physical dimensions and the ISO 7811 for the positioning and the structure of the magnetic stripe data. This standard divides the magnetic strip into three tracks:
- ISO 1 track, IATA (International Air Transportation Association), maximum 70 7-bit characters;
- ISO 2 track, ABA (American Bankers Association), maximum 40 5-bit characters;
- ISO 3 track, MINTS (Mutual Institution National Transfer System), maximum 107 5-bit characters.
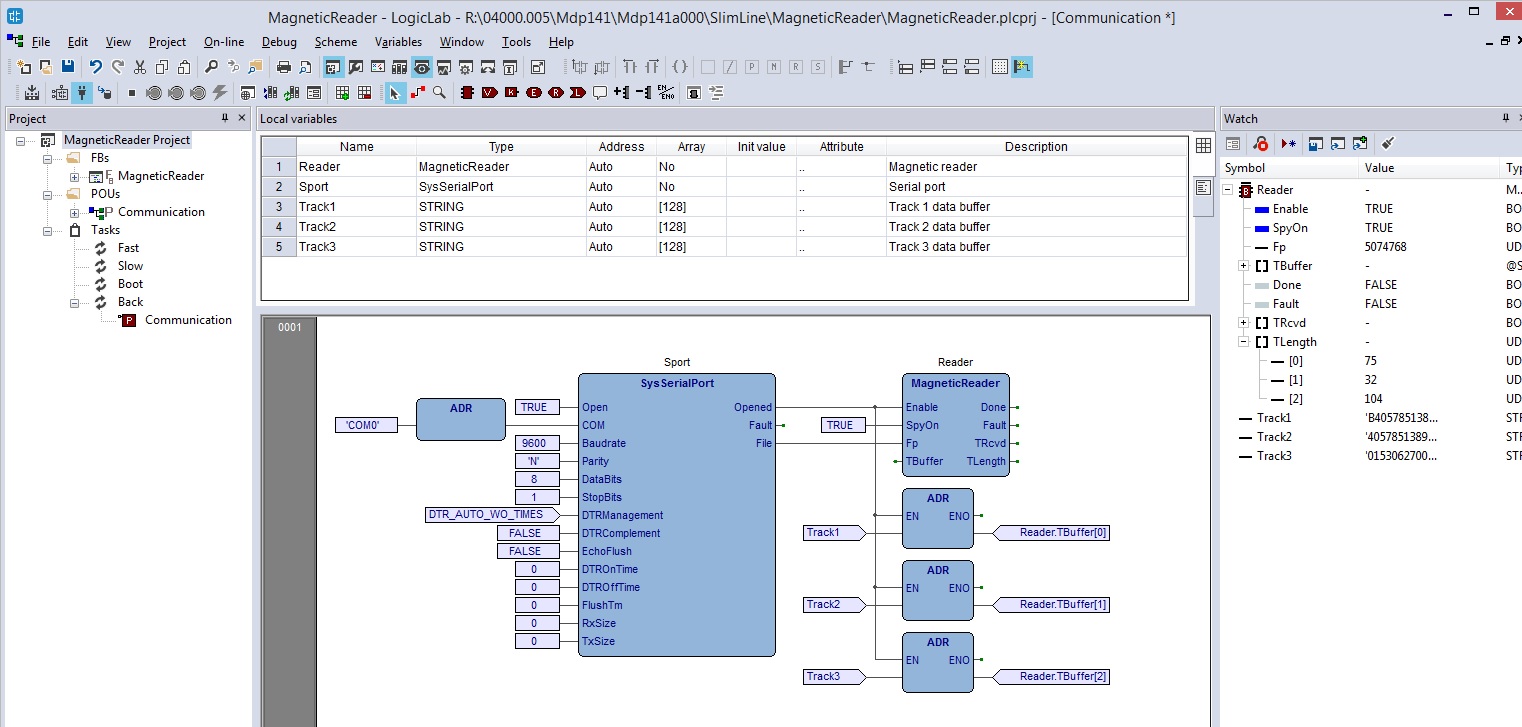
Here is the screenshot of the project MagneticReader that manages the reading of all 3 traces of a magnetic card. The reader is connected to the COM0 port and an FB provides for its management. The FB addresses the addresses of the buffers in which to transfer the data read from the 3 tracks, see project on GitHub.