Con il termine SHA (acronimo dell’inglese Secure Hash Algorithm) si indicano funzioni crittografiche di hash. L’SHA produce un message digest, o “impronta del messaggio”, di lunghezza fissa partendo da un messaggio di lunghezza variabile. La sicurezza dell’algoritmo risiede nel fatto che la funzione non è invertibile (non è possibile risalire al messaggio originale) e non è possibile avere lo stesso digest da messaggi diversi.
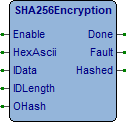
Attivando Enable verrà eseguito il calcolo dell’hash del file indicato in IData (Se IDLength=0) oppure dell’area di memoria o stringa indicata in IData (Se Length<>0) in tal caso IDLength deve indicare la dimensione dell’area su cui eseguire il calcolo.
Terminata l’esecuzione o su errore si attiva l’uscita Done, se il calcolo è stato eseguito correttamente si attiva anche l’uscita Hashed. Le uscite rimangono attive fino alla disabilitazione di Enable. Per eseguire un nuovo calcolo occorre disabilitare e poi riabilitare Enable.
Descrizione
Enable (BOOL) Comando calcolo hasvh.
HexAscii (BOOL) Seleziona il tipo di hash in uscita. FALSE: viene ritornato in esadecimale (BYTE[32]). TRUE: Viene ritornato in ascii (STRING[64]).
IData (@eVOID) Ha due significati in base al valore di IDLength. IDLength=0: File su cui calcolare l’hash. IDLength<>0 Indirizzo stringa su cui calcolale l’hash.
IDLength (UDINT) Settare 0 se si desidera calcolare l’hash di un file. Se si calcola l’hash di una stringa o di un’area di memoria occorre definire la dimensione dell’area.
OHash (@eVOID) Definire l’indirizzo del buffer dove il FB andrà a scrivere il valore di hash calcolato. Deve essere un array di 32 BYTES nel caso di uscita esadecimale, o una STRING di 64 caratteri nel caso di uscita ascii.
Done (BOOL) Si attiva al termine della esecuzione.
Fault (BOOL) Attivo per un loop in caso di errore esecuzione.
Hashed (BOOL) Attivo se calcolo terminato correttamente.
Esempi
Come utilizzare gli esempi.
Nell’esempio attivando Execute da debug viene calcolato l’hash su di un file e su una stringa. Per testare l’esempio occorre trasferire sul disco D: un file di testo Hash.txt di 73 caratteri con il testo: “Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusanti.” Nell’esempio viene anche calcolato il tempo necessario ad eseguire l’hash.
LogicLab (Ptp179)
PROGRAM ST_SHA256Encryption
VAR
Execute : BOOL; (* Execute command *)
Ok : ARRAY[0..1] OF BOOL; (* Hash Ok *)
FHash : STRING[ 64 ]; (* File hash *)
CaseNr : USINT; (* Program case *)
TimeBf : UDINT; (* Time buffer (uS) *)
Time : ARRAY[0..1] OF REAL; (* Required time (S) *)
SHash : STRING[ 64 ]; (* String hash *)
SHA256 : SHA256Encryption; (* SHA256 encryption *)
END_VAR
// *****************************************************************************
// PROGRAM "ST_SHA256Encryption"
// *****************************************************************************
// This program demonstrate the use of the SHA256 encryption function block. It
// calculates the SHA256 on a text file and a string. To be used a 73 characters
// file named "Hash.txt" must be loaded on "C:" disk. The file content must be:
//
// "Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusanti."
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// SHA256 HASH ENCRYPTION
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Execute the SHA256 encryption.
SHA256(); //SHA256 encryption
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// PROGRAM LOOP
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Manage program cases.
CASE (CaseNr) OF
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// CALCULATE SHA256 ON A FILE
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Calculate SHA256 hash of a file.
0:
IF NOT(Execute) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
TimeBf:=SysGetSysTime(TRUE); //Time buffer (uS)
SHA256.HexAscii:=TRUE; //Ascii output
SHA256.IData:=ADR('D:/Hash.txt'); //Input data pointer
SHA256.IDLength:=0; //Input data length (Set 0 to use a file)
SHA256.OHash:=ADR(FHash); //Output hash pointer
SHA256.Enable:=TRUE; //SHA256 enable
CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; //Program case
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Wait the end and calculate the required time.
1:
IF NOT(SHA256.Done) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
SHA256.Enable:=FALSE; //SHA256 enable
Time[0]:=TO_REAL(SysGetSysTime(TRUE)-TimeBf)/1000000.0; //Required time (S)
// Check if result is correct.
IF (SHA256.Hashed) THEN
IF (FHash = 'a6652be5e5c41d533fa91690b3e88ee49144d485b1e4b0c328f54b6454ecdcad') THEN Ok[0]:=TRUE; END_IF;
END_IF;
CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; //Program case
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// CALCULATE SHA256 ON A STRING
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Calculate SHA256 hash of a string.
2:
TimeBf:=SysGetSysTime(TRUE); //Time buffer (uS)
SHA256.HexAscii:=TRUE; //Ascii output
SHA256.IData:=ADR('Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.'); //Input data pointer
SHA256.IDLength:=Sysstrlen(SHA256.IData); //Input data length
SHA256.OHash:=ADR(SHash); //Output hash pointer
SHA256.Enable:=TRUE; //SHA256 enable
CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; //Program case
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Wait the end and calculate the required time.
3:
IF NOT(SHA256.Done) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
SHA256.Enable:=FALSE; //SHA256 enable
Time[1]:=TO_REAL(SysGetSysTime(TRUE)-TimeBf)/1000000.0; //Required time (S)
// Check if result is correct.
IF (SHA256.Hashed) THEN
IF (SHash = '1d32dc481e105799b079b5a1b18c2e302bc43bc5feac01450c7ffa50a1c65b92') THEN Ok[1]:=TRUE; END_IF;
END_IF;
Execute:=FALSE; //Execute command
CaseNr:=0; //Program case
END_CASE;
// [End of file]