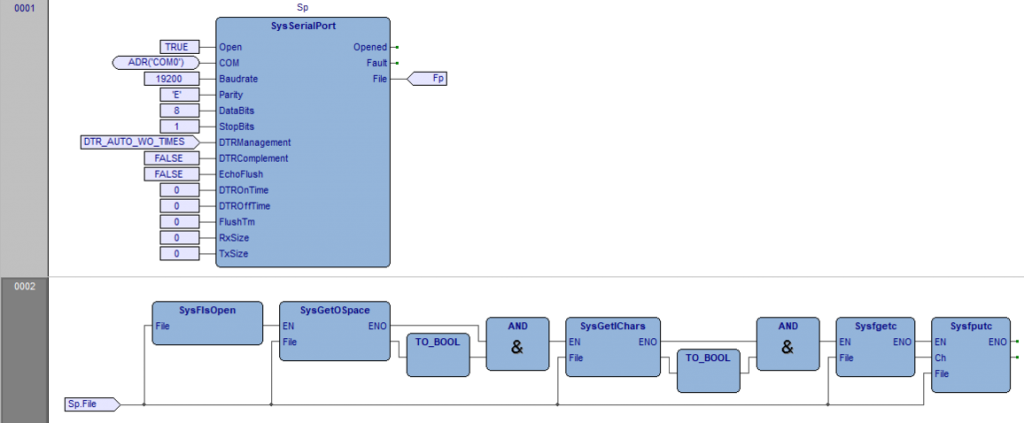
Questo blocco funzione gestisce la comunicazione su porta seriale, occorre definire in COM la porta da gestire fornendo tutti i parametri di configurazione. Se non sono definiti parametri la porta verrà impostata di default a 19200, e, 8, 1, DTR_AUTO_WO_TIMES.
Attivando il comando Open la porta viene aperta se non ci sono problemi viene attivato Opened e sull’uscita File viene ritornato lo stream da utilizzarsi per lo scambio dati sulla porta. Se ci sono errori nei parametri o con la porta definita viene generato Fault.
Per aggiungere porte seriali ai nostri moduli CPU è possibile utilizzare convertitori USB/Seriale sui moduli basati su Linux e convertitori Ethernet/Seriale sui moduli ARM e Cortex, vedi articolo.
Approfondimenti
- Per gestire lo stream di I/O eFILEP in uscita dal FB puoi utilizzare gli oggetti di gestione dei terminali (Streams) di I/O.
- In questo articolo un programma di esempio per lo sviluppo di un driver di comunicazione seriale.
LogicLab (Ptp116, ST_SerialDataReceive) Semplice protocollo seriale
Riportiamo un programma che gestisce un semplice protocollo seriale, viene ricevuta una stringa con 2 valori REAL. I valori ricevuti sono decodificati e ritornati in risposta.
PROGRAM ST_SerialDataReceive
VAR
Ch : BYTE; (* Rx character *)
ErrorNr : USINT; (* Error number *)
CaseNr : USINT; (* Program case *)
RxCtr : UDINT; (* Rx data counter *)
Ptr : PVOID; (* Auxiliary buffer *)
SpyBuffer : STRING[ 64 ]; (* Spy buffer *)
RxTxBuf : STRING[ 128 ]; (* Rx/Tx data buffer *)
Value : ARRAY[0..1] OF REAL; (* Value array *)
TimeBf : ARRAY[0..1] OF UDINT; (* Time buffer (mS) *)
Sp : SysSerialPort; (* Serial port management *)
END_VAR
// *****************************************************************************
// PROGRAM "ST_SerialDataReceive"
// *****************************************************************************
// Receives data from serial port and manage them.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// INITIALIZATION
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Configure serial port.
IF (SysFirstLoop) THEN
Sp.COM:=ADR('COM0'); //COM port definition
// Sp.COM:=ADR('/dev/ttyAMA0'); //COM port definition
// Sp.COM:=ADR('/dev/ttyUSB0'); //COM port definition
Sp.Baudrate:=19200; //Baudrate
Sp.Parity:='E'; //Parity
Sp.DataBits:=8; //Data bits
Sp.StopBits:=1; //Stop bits
Sp.DTRManagement:=DTR_AUTO_WO_TIMES; //DTR management
Sp.DTRComplement:=FALSE; //DTR complement
Sp.EchoFlush:=FALSE; //Received echo flush
Sp.DTROnTime:=0; //DTR On time delay (mS)
Sp.DTROffTime:=0; //DTR Off time delay (mS)
Sp.FlushTm:=0; //Flush time (mS)
Sp.RxSize:=0; //Rx buffer size
Sp.TxSize:=0; //Tx buffer size
END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// MANAGE THE SERIAL PORT
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Manage the serial port.
Sp(Open:=TRUE); //Serial port management
IF NOT(Sp.Opened) THEN CaseNr:=0; RETURN; END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// EXECUTION ERROR REPORT
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// On execution error the reception loop is ended and the error number is
// reported on spy console
IF (ErrorNr <> 0) THEN
eTO_JUNK(SysVsnprintf(ADR(SpyBuffer), SIZEOF(SpyBuffer), ADR('Error:%d'), USINT_TYPE, ADR(ErrorNr)));
eTO_JUNK(SysCVsnprintf(ADR(SpyBuffer), SIZEOF(SpyBuffer), ADR(', On case:%d'), USINT_TYPE, ADR(CaseNr)));
eTO_JUNK(SysWrSpyData(SPY_ASCII, 0, 16#10000000, ADR('SerialDataReceive:Er'), ADR(SpyBuffer)));
ErrorNr:=0; //Error number
CaseNr:=0; //Program case
END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// CASE LOOP
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// If reception starts it must be ended in a defined time.
IF (CaseNr = 0) THEN TimeBf[0]:=SysTimeGetMs(); END_IF;
IF ((SysTimeGetMs()-TimeBf[0]) > TO_UDINT(T#1s)) THEN
ErrorNr:=10; //Error number
RETURN;
END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// CASE MANAGEMENRT
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Program cases.
CASE (CaseNr) OF
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// WAITS RECEPTION START
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Waits until a first character is been received.
0:
IF NOT(TO_BOOL(SysFGetIChars(Sp.File))) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
eTO_JUNK(Sysmemset(ADR(RxTxBuf), 0, SIZEOF(RxTxBuf))); //Clear data buffer
Ch:=TO_BYTE(Sysfgetc(Sp.File)); //Rx character
// In the example is received a plain string is managed, but if the
// string starts with a defined character, it must be waited here.
// IF (Ch <> 16#02) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
// Initialize the reception.
eTO_JUNK(eSetBYTE(ADR(RxTxBuf), Ch)); //Store character in buffer
RxCtr:=1; //Rx data counter
CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; //Program case
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// In some cases reception ends when no characters has been received for
// a defined time.
1:
IF NOT TO_BOOL(SysFGetIChars(Sp.File)) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
// IF ((SysTimeGetMs()-TimeBf[1]) > TO_UDINT(T#100ms)) THEN CaseNr:=10; RETURN; END_IF;
// Here the string is received.
WHILE TO_BOOL(SysFGetIChars(Sp.File)) DO
TimeBf[1]:=SysTimeGetMs(); //Time buffer (mS)
Ch:=TO_BYTE(Sysfgetc(Sp.File)); //Rx character
eTO_JUNK(eSetBYTE(ADR(RxTxBuf)+RxCtr, Ch)); //Store character in buffer
RxCtr:=RxCtr+1; //Rx data counter
// If the string end with a defined character, it must be verified.
// Plain string usually terminates with a .
IF (Ch = 16#0D) THEN CaseNr:=10; RETURN; END_IF;
// If a defined number of character is expected, when has been
// received reception ends
// IF (RxTxCtr = 15) THEN CaseNr:=10; RETURN; END_IF;
// Check if string is longer than defined buffer.
IF (RxCtr >= SIZEOF(RxTxBuf)) THEN
ErrorNr:=20; //Error number
RETURN;
END_IF;
END_WHILE;
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
// Here the string has been received, it's sent to spy console.
10:
eTO_JUNK(SysWrSpyData(SPY_ASCHEX, 0, 16#00000001, ADR('SerialDataReceive:Rx'), ADR(RxTxBuf)));
// Assuming string as an array of numbers here they are decoded.
// "Value:10.23, Value:456.56..."
Ptr:=SysStrFind(ADR(RxTxBuf), ADR('Value:'), FIND_GET_END);
IF (Ptr = eNULL) THEN ErrorNr:=20; RETURN; END_IF;
IF NOT(SysVsscanf(Ptr, ADR('%f'), REAL_TYPE, ADR(Value[0]))) THEN ErrorNr:=21; RETURN; END_IF;
Ptr:=SysStrFind(Ptr, ADR('Value:'), FIND_GET_END);
IF (Ptr = eNULL) THEN ErrorNr:=30; RETURN; END_IF;
IF NOT(SysVsscanf(Ptr, ADR('%f'), REAL_TYPE, ADR(Value[1]))) THEN ErrorNr:=31; RETURN; END_IF;
CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; //Program case
// -----------------------------------------------------------------
// Waits for space on tx buffer
11:
IF (TO_UDINT(SysFGetOSpace(Sp.File)) <> SysFGetOBfSize(Sp.File)) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
// Printout the received values.
eTO_JUNK(SysVsnprintf(ADR(RxTxBuf), SIZEOF(RxTxBuf), ADR('Values [0]:%5.2f'), REAL_TYPE, ADR(Value[0])));
eTO_JUNK(SysCVsnprintf(ADR(RxTxBuf), SIZEOF(RxTxBuf), ADR(', [1]:%6.2f$r$n'), REAL_TYPE, ADR(Value[1])));
eTO_JUNK(Sysfwrite(ADR(RxTxBuf), TO_INT(Sysstrlen(ADR(RxTxBuf))), 1, Sp.File));
CaseNr:=0; //Program case
END_CASE;
// [End of file]Descrizione
Open (BOOL) Comando apertura porta seriale.
COM (@STRING) Definizione della porta COM da utilizzare (Su CODESYS diventa pCOM).
Baudrate (UDINT) Valore di baud rate porta seriale (da 300 a 115200 baud).
Parity (STRING[1]) Tipo di parità, valori possibili “E” pari, “O” dispari, “N” nessuna.
DataBits (USINT) Numero di bit frame dato, valori possibili 7, 8.
StopBits (USINT)) Numero di bit di stop, valori possibili 1, 2.
DTRManagement (DTR_MODE) Modo di gestione del segnale DTR sulla porta seriale (Definizione).
DTRComplement (BOOL) FALSE: DTR normale, TRUE: DTR complementato.
EchoFlush (BOOL) FALSE: I dati trasmessi sono ritornati in ricezione. TRUE: I dati trasmessi sono ignorati. Questa impostazione è utile nelle comunicazione RS485 per non ricevere in echo i dati trasmessi.
DTROnTime (UINT) Tempo di attesa dopo attivazione segnale DTR prima di trasmissione caratteri (mS).
DTROffTime (UINT) Tempo di attesa dopo trasmissione ultimo dato prima e disattivazione segnale DTR (mS).
FlushTm (UINT) Tempo di flush dati, se non sono caricati dati sullo stream dopo il tempo definito i dati presenti vengono automaticamente inviati (mS) (Impostare 0).
RxSize (UINT) Dimensione buffer ricezione dati.
TxSize (UINT) Dimensione buffer trasmissione dati.
Opened (BOOL) Attivo se porta porta seriale aperta.
Fault (BOOL) Attivo se errore gestione.
File (FILEP) Stream di I/O. Viene valorizzato su apertura porta seriale.
LogicLab, definizione porta COM
La porta da utilizzare và definita nel parametro COM, il valore cambia in funzione del sistema che si stà utilizzando.
| SlimLine compact senza ethernet | COM0 (Rs232 su P4), COM2 (Rs485 su P2 se prevista) |
| SlimLine compact con ethernet | COM0 (Rs232 su P4) |
| SlimLine Cortex M7 | COM0 (Rs232 su P4), COM1 (Rs232 su P5), COM2 (Rs485 su P2 se prevista) |
| Netlog III | COM0 (Rs232 su Port A), PCOM0.0 (Rs232 su Port B), COM2 (Rs485 su P9 se prevista) |
| SlimLine Raspberry | /dev/ttyAMA0 (Rs485 su P2 se prevista) |
Lo SlimLine basato su Raspberry permette di aumentare il numero di porte connettendo al sistema dei convertitori USB/Seriale. Le porte aggiuntive assumeranno un identificativo assegnato automaticamente (Avremo /dev/ttyUSB0, /dev/ttyUSB1, ecc). Connesso il convertitore al modulo, da console SSH con il comando lsusb è possibile vedere se è stato riconosciuto. Ecco il comando eseguito su di un modulo a cui è stato connesso un convertitore.
lsusb Bus 001 Device 008: ID 0403:6001 Future Technology Devices International, Ltd FT232 USB-Serial (UART) IC
Per conoscere il nome assegnato alla porta eseguire un listing della directory /dev, ecco il comando:
ls /dev | grep ttyUSB ttyUSB0 ttyUSB1
In questo caso al modulo sono stati connessi 2 convertitori USB/Seriale e le porte sono identificate con /dev/ttyUSB0 e /dev/ttyUSB1.
CODESYS, definizione porta pCOM
Porta seriale RS485
Se il dispositivo SlimLine dispone di porta seriale RS485, la porta è conessa alla porta ttyAMA del modulo CPU Raspberry, per poterla utilizzare dall’ambiente CODESYS identificandola come “1”, occorre nel file /etc/CODESYSControl_User.cfg modificare la voce [SysCom] come indicato di seguito. Nota si specifica device ttyAMA anche se il device è ttyAMA0.
[SysCom] ;Linux.Devicefile=/dev/ttyS Linux.Devicefile=/dev/ttyAMA
Aggiungere porta seriale su USB
Utilizzando moduli USB/Seriale è possibile connettere alla porta USB del modulo porte seriali aggiuntive, nel caso di una porta da utilizzare in alternativa alla ttyAMA identificandola come “1”, occorre modificare la voce [SysCom] come indicato di seguito. Nota si specifica device ttyUSB anche se il device è ttyUSB0.
[SysCom] ;Linux.Devicefile=/dev/ttyS Linux.Devicefile=/dev/ttyUSB
Esempi
Oltre al programma di esempio ST_SerialDataReceive riportato in testa all’articolo rimando al programma ST_WindSonicDriver. Entrambi questi programmi aiutano a capire nel dettaglio come gestire le comunicazioni seriali.Negli esempi seguenti viene aperta una porta di comunicazione seriale e viene eseguito l’echo dei caratteri ricevuti.
LogicLab (Ptp116), ST_SysSerialPort
PROGRAM ST_SysSerialPort
VAR
Ch : INT; (* Auxiliary variable *)
Sp: SysSerialPort; (* Serial port management *)
END_VAR
// *****************************************************************************
// PROGRAM "ST_SysSerialPort"
// *****************************************************************************
// This program echoes the characters received by the serial line.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// INITIALIZATION
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
IF (SysFirstLoop) THEN
Sp.COM:=ADR('COM0'); //COM port definition
// Sp.COM:=ADR('/dev/ttyAMA0'); //COM port definition
// Sp.COM:=ADR('/dev/ttyUSB0'); //COM port definition
Sp.Baudrate:=19200; //Baudrate
Sp.Parity:='E'; //Parity
Sp.DataBits:=8; //Data bits
Sp.StopBits:=1; //Stop bits
Sp.DTRManagement:=DTR_AUTO_WO_TIMES; //DTR management
Sp.DTRComplement:=FALSE; //DTR complement
Sp.EchoFlush:=FALSE; //Received echo flush
Sp.DTROnTime:=0; //DTR On time delay (mS)
Sp.DTROffTime:=0; //DTR Off time delay (mS)
Sp.FlushTm:=0; //Flush time (mS)
Sp.RxSize:=0; //Rx buffer size
Sp.TxSize:=0; //Tx buffer size
END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ECHOES CHARACTERS
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Here the received characters are echoed back.
Sp(Open:=TRUE); //Serial port management
IF (Sp.Opened) THEN
IF ((SysFGetOSpace(Sp.File) > 0) AND (SysFGetIChars(Sp.File) > 0)) THEN
Ch:=Sysfgetc(Sp.File); //Get input character
Ch:=Sysfputc(Ch, Sp.File); //Put input character
END_IF;
END_IF;
// [End of File]CODESYS (Ptp161), ST_SysSerialPort
PROGRAM ST_SysSerialPort
VAR
FirstLoop: BOOL := TRUE; // First execution loop
Ch : INT; //Auxiliary variable
Sp: SysSerialPort; //Serial port management
END_VAR
// *****************************************************************************
// PROGRAM "ST_SysSerialPort"
// *****************************************************************************
// This program echoes the characters received by the serial line.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// INITIALIZATION
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Initialize the serial port.
IF (FirstLoop) THEN
FirstLoop:=FALSE; //First execution loop
Sp.pCOM:=ADR('1'); //COM port definition
Sp.Baudrate:=19200; //Baudrate
Sp.Parity:='E'; //Parity
Sp.DataBits:=8; //Data bits
Sp.StopBits:=1; //Stop bits
Sp.DTRManagement:=DTR_MODE.DTR_AUTO_WO_TIMES; //DTR management
Sp.DTRComplement:=FALSE; //DTR complement
Sp.EchoFlush:=FALSE; //Received echo flush
Sp.DTROnTime:=0; //DTR On time delay (mS)
Sp.DTROffTime:=0; //DTR Off time delay (mS)
Sp.FlushTm:=0; //Flush time (mS)
Sp.RxSize:=0; //Rx buffer size
Sp.TxSize:=0; //Tx buffer size
END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// ECHOES CHARACTERS
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Here the received characters are echoed back.
Sp(Open:=TRUE); //Serial port management
IF (Sp.Opened) THEN
IF ((SysFGetOSpace(Sp.File) > 0) AND (SysFGetIChars(Sp.File) > 0)) THEN
Ch:=Sysfgetc(Sp.File); //Get input character
Ch:=Sysfputc(Ch, Sp.File); //Put input character
END_IF;
END_IF;
// [End of File]