Libreria gestione SNMP (eLLabSNMPLib)¶
Attenzione! Per utilizzare la libreria occorre importarla nel proprio progetto. Vedere capitolo relativo all”import delle librerie.
Il Simple network management protocol (spesso abbreviato in Snmp) è un dei protocolli di Rete appartenenti alla suite TCP/IP e operante al livello 7 del modello ISO/OSI. Lo SNMP consente la configurazione, la gestione e la supervisione di dispositivi di rete collegati a una LAN o a una rete geografica più estesa. Solitamente, il protocollo è supportato da dispositivi quali router, switch di rete, server, stampanti di rete e altri. Il Simple network management protocol permette agli amministratori di rete e ai sistemisti di tenere sotto controllo le performance della rete, risolvere eventuali problematiche e pianificare uno sviluppo futuro della rete.
Questa libreria pubblica oggetti per gestire il protocollo sia lato Server (Agent) che lato Client (Manager).
Agent: Permette l’accesso all’informazione da gestire da parte delle applicazioni esterne permette la modifica dei parametri di funzionamento e fornisce funzioni di polling, misura, monitoraggio, statistiche.
Manager: Anche chiamato Management Station agisce come punto di raccolta e di elaborazione delle informazioni ricavate dai vari Agent degli apparati.
PDUType, definizione tipo query SNMP¶
Le query supportate dal gestore SNMP manager sono riportate nella tabella seguente.
| PDUType | Function | Description |
| 16#A0 | GetRequest | This PDU is sent from a management station to the agent and is used to retrieve the values of object instances whose OIDs are contained in the PDU. |
| 16#A1 | GetNextRequest | This PDU is sent from a management station to the agent and is used to retrieve the values of the object instances whose OIDs are lexicographically next to that of the OID contained in the PDU. |
| 16#A3 | SetRequest | This PDU is sent from a management station to the agent and is used to set the values of object instances whose OIDs and value are contained in the PDU. |
VType, definizione tipo variabile¶
Il gestore SNMP manager opera solo su alcuni tipi di variabili in funzione del Data Type gestito nel frame SNMP.
| VType | Value | Description |
| SNMP_VT_INTEGER | 16#02 | Integer: Must refer to a signed 32bit Integer DINT variable. (Values between -2147483648 and 2147483647). |
| SNMP_VT_STRING | 16#04 | Octect string: Must refer to a STRING variable. Arbitrary binary or textual data, typically limited to 255 characters in length. |
| SNMP_VT_NULL | 16#05 | Null: Must refer to a Null pointer. |
| SNMP_VT_IPADDRESS | 16#40 | IPAddress: Must refer to a STRING variable. An IP address in textual data, limited to 15 characters length. |
| SNMP_VT_COUNTER32 | 16#41 | Counter32: Must refer to a unsigned 32bit Integer UDINT variable. Represents a non-negative integer which monotonically increases until it reaches a maximum value of 32bits-1 (4294967295 dec), when it wraps around and starts increasing again from zero. |
| SNMP_VT_GAUGE32 | 16#42 | Gauge32: Must refer to a unsigned 32bit Integer UDINT variable. Represents a non-negative integer, which holds at the maximum or minimum value specified in the range when the actual value goes over or below the range, respectively. |
| SNMP_VT_TIMETICKS | 16#43 | TimeTicks: Must refer to a unsigned 32bit Integer UDINT variable. Represents an unsigned integer which represents the time, in hundredths of a second between two epochs. |
ECode, definizione codice errore¶
Viene ritornato il codice di errore ricevuto da Agent.
| ECode | Error | Descritption |
| 0 | noError | No error occurred. This code is also used in all request PDUs, since they have no error status to report. |
| 1 | tooBig | The size of the Response-PDU would be too large to transport. |
| 2 | noSuchName | The name of a requested object was not found. |
| 3 | badValue | A value in the request didn’t match the structure that the recipient of the request had for the object. For example, an object in the request was specified with an incorrect length or type. |
| 4 | readOnly | An attempt was made to set a variable that has an Access value indicating that it is read-only. |
| 5 | genErr | An error occurred other than one indicated by a more specific error code in this table. |
| 6 | noAccess | Access was denied to the object for security reasons. |
| 7 | wrongType | The object type in a variable binding is incorrect for the object. |
| 8 | wrongLength | A variable binding specifies a length incorrect for the object. |
| 9 | wrongEncoding | A variable binding specifies an encoding incorrect for the object. |
| 10 | wrongValue | The value given in a variable binding is not possible for the object. |
| 11 | noCreation | A specified variable does not exist and cannot be created. |
| 12 | inconsistentValue | A variable binding specifies a value that could be held by the variable but cannot be assigned to it at this time. |
| 13 | resourceUnavailable | An attempt to set a variable required a resource that is not available. |
| 14 | commitFailed | An attempt to set a particular variable failed. |
| 15 | undoFailed | An attempt to set a particular variable as part of a group of variables failed, and the attempt to then undo the setting of other variables was not successful. |
| 16 | authorizationError | A problem occurred in authorization. |
| 17 | notWritable | The variable cannot be written or created. |
| 18 | inconsistentName | The name in a variable binding specifies a variable that does not exist. |
SNMPVARIABLEDEFS, definizione variabile SNMP¶
Questo tipo di dati è utilizzato dal blocco funzione SNMPAgent per la definizione degli oggetti gestiti.
| Name | Type | Description |
| Type | USINT | Tipo variabile (`Vedi tabella <#vtype-defin izione-tipo-variabile >`__). |
| Writable | BOOL | Se TRUE la variabile può essere scritta. |
| OID | @USINT | Indirizzo stringa definizione Object Identifier. |
| Address | @USINT | Indirizzo allocazione variabile. |
| Length | UDINT | Lunghezza variabile. |
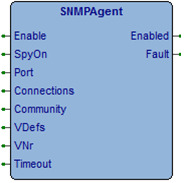
SNMPAgent, manages the SNMP Agent¶
| Type | Library |
| FB | eLLabSNMPLib_A000 |
Questo blocco funzione esegue la gestione del protocollo SNMP agendo come Agent. Attivando l’FB si pone in ascolto l’agente sulla porta definita, sono accettate il numero di connessioni contemporanee definite in Connections.
In Community occorre definire l’indirizzo della stringa di definizione della comunità accettata dall’Agent.
Per la definizione delle variabili gestite dall’Agent è definita nella libreria una apposita struttura dati. La struttura SNMPVARIABLEDEFS permette di definire le variabili su cui l’Agent può operare. In VDefs occorre fornire l’indirizzo di allocazione della struttura di definizione variabili ed in VNr occorre definire il numero delle variabili definite.
Il FB gestisce autonomamente il comando SnmpWalk permettendo di “camminare” tra tutte le variabili definite.
| Enable (BOOL) | Comando attivazione SNMP Agent. |
| SpyOn (BOOL) | Se attivo permette di spiare il funzionamento della FB. |
| Port (UINT) | Porta UDP su cui porre in ascolto l’Agent. Solitamente si utilizza la porta 161. |
| Connections (USINT) | Numero di connessioni contemporanee gestite dal FB (Da 1 a 4). |
| Community (@USINT) | Indirizzo allocazione stringa definizione Community. |
| VDefs (@SNMPVARIABLEDEFS) | Indirizzo allocazione struttura SNMPVARIABLEDEFS. |
| VNr (USINT) | Numero di variabili definite. |
| Timeout (UINT) | Timeout esecuzione query SNMP (mS). |
| Enabled (BOOL) | Blocco funzione abilitato. |
| Fault (BOOL) | Attivo per un loop di programma se errore gestione. |
Codici di errore
In caso di errore si attiva l’uscita Fault, con SysGetLastError è possibile rilevare il codice di errore.
| Codice | Descrizione |
| 10059020 | FB eseguita in una task diversa dalla task di background. |
| 10059030 | Connections non impostato correttamente. |
| 10059080 | Timeout esecuzione. |
| 10059090 | Errore interno. |
| 10059100~2 | Errore ricezione intestazione frame SNMP da Manager. |
| 10059110 | PDU type ricevuto non gestito. |
| 10059200~99 | Errore nella decodifica del comando SNMP ricevuto da Manager. |
| 10059300~99 | Errore nella codifica della risposta SNMP verso Manager. |
Esempi¶
Nell’esempio viene gestito un agente SNMP, l’agente opera su due variabili.
Definizione variabili
Esempio ST (PTP137A000, ST_SNMPAgent)
(\* Program initialization \*)
IF (SysFirstLoop) THEN
(\* Parametrize the SNMP Agent FB. \*)
SNMPAgt.SpyOn:=TRUE; (\* Spy command \*)
SNMPAgt.Port:=161; (\* Agent port \*)
SNMPAgt.Connections:=2; (\* Accepted connections \*)
SNMPAgt.Community:=ADR('public'); (\* Community \*)
SNMPAgt.VDefs:=ADR(VDefs); (\* Variable definitions \*)
SNMPAgt.VNr:=2; (\* Variable number \*)
SNMPAgt.Timeout:=1000; (\* Timeout (mS) \*)
(\* Definition of the variables on wich the Agent can operate. \*)
VDefs[0].Type:=16#02; (\* Variable type \*)
VDefs[0].Writable:=TRUE; (\* Variable can be written \*)
VDefs[0].OID:=ADR('1.3.6.1.4.1.36955.1'); (\* OID definition \*)
VDefs[0].Address:=ADR(Value); (\* Variable address \*)
VDefs[0].Length:=SIZEOF(Value); (\* Variable length \*)
VDefs[1].Type:=16#04; (\* Variable type \*)
VDefs[1].Writable:=FALSE; (\* Variable cannot be written \*)
VDefs[1].OID:=ADR('1.3.6.1.4.1.36955.2'); (\* OID definition \*)
VDefs[1].Address:=ADR('Hello!'); (\* Variable address \*)
VDefs[1].Length:=Sysstrlen(VDefs[1].Address); (\* Variable length \*)
END_IF;
(\* Manage the SNMP Agent. \*)
SNMPAgt(Enable:=TRUE); (\* SNMP Agent \*)
(\* [End of file] \*)
Ecco il risultato di un comando SnmpWalk inviato all’Agent:
SnmpWalk -r:192.168.0.181
SnmpWalk v1.01 - Copyright (C) 2009 SnmpSoft Company
OID=.1.3.6.1.4.1.36955.1, Type=Integer, Value=-1350
OID=.1.3.6.1.4.1.36955.2, Type=OctetString, Value=Hello!
Total: 2
_section-1:
SNMPManager, sends a SNMP message¶
| Type | Library |
| FB | eLLabSNMPLib_A000 |
Questo blocco funzione esegue la gestione del protocollo SNMP agendo come Manager. Attivando l’FB viene inviato un pacchetto SNMP con il valore di PDUType indicato. Eseguito l’invio e ricevuta la richiesta dall’Agent viene attivata l’uscita Done. Per inviare un nuovo pacchetto occorre disabilitare e poi riabilitare Enable.
Attivando Enable viene inviato all’Agent con indirizzo Address sulla porta Port il messaggio SNMP di tipo PDUType con OID definito.
Se il messaggio è di tipo lettura, al termine, nella variabile indicata sarà trasferito il valore della variabile acquisita dall’Agent.
Se il messaggio è di tipo scrittura, al termine il valorte della variabile definita sarà stato trasferito nell’Agent.
In Community occorre definire l’indirizzo della stringa di definizione della comunità accettata dall’Agent.
| Enable (BOOL) | Comando attivazione SNMP Manager. |
| SpyOn (BOOL) | Se attivo permette di spiare il funzionamento della FB. |
| Address (@USINT) | Indirizzo IP o URL dell’Agent a cui inviare la query SNMP. |
| Port (UINT) | Porta UDP a cui inviare la query. Solitamente si utilizza la porta 161. |
| Community (@USINT) | Indirizzo allocazione stringa definizione Community. |
| PDUType (USINT) | Tipo di query SNMP da inviare (Vedi tabella). |
| OID (@USINT) | Indirizzo stringa definizione Object Identifier da richiedere. |
| VType (USINT) | Tipo variabile ricevuta/da inviare (Vedi tabella). |
| VAddress (@USINT) | Indirizzo allocazione variabile ricevuta/da inviare. |
| VLength (UDINT) | Lunghezza variabile ricevuta/da inviare. |
| Timeout (UINT) | Timeout esecuzione query SNMP (mS). |
| Done (BOOL) | Esecuzione comando terminata. |
| Ok (BOOL) | Attivo per un loop di programma se comando eseguito correttamente. |
| Fault (BOOL) | Attivo per un loop di programma se errore gestione. |
| ECode (USINT) | Riporta l’eventuale codice di errore ricevuto dall’Agent (Vedi tabella). |
| EIndex (USINT) | Riporta l’eventuale indice di errore ricevuto dall’Agent. |
Codici di errore
In caso di errore si attiva l’uscita Fault, con SysGetLastError è possibile rilevare il codice di errore.
| Codice | Descrizione |
| 10060020 | FB eseguita in una task diversa dalla task di background. |
| 10060080 | Timeout esecuzione. |
| 10060090 | Errore interno. |
| 10060100~99 | Errore nella codifica del comando SNMP verso Agent. |
| 10060200~2 | Errore ricezione intestazione frame risposta SNMP da Agent. |
| 10060300~99 | Errore nella decodifica della risposta SNMP ricevuta da Agent. |
| 10060400~9 | Errore dati nella risposta SNMP ricevuta da Agent. |
| 10060410~9 | Errore impostazione VType. |
| 10060420~9 | Errore impostazione VLength. |
Esempi¶
Nell’esempio viene eseguita una richiesta SNMP verso un Agent su un altro sistema SlimLine. Attivando Di00CPU viene richiesto l’OID 1.3.6.1.4.1.36955.2 su di un sistema SlimLine dove è in esecuzione il programma Agent. L’agente risponderà inviando una variabile stringa con contenuto “Hello!”.
Definizione variabili
Esempio ST (PTP137A000, ST_SNMPManager)
(\* Program initialization \*)
IF (SysFirstLoop) THEN
SNMPMng.Port:=161; (\* Peer port \*)
SNMPMng.SpyOn:=TRUE; (\* Spy command \*)
SNMPMng.PDUType:=16#A0; (\* PDU type \*)
SNMPMng.Community:=ADR('public'); (\* Community \*)
SNMPMng.Timeout:=1000; (\* Execution timeout (mS) \*)
SNMPMng.VType:=16#04; (\* Variable type \*)
SNMPMng.VLength:=SIZEOF(Str); (\* Variable length \*)
SNMPMng.VAddress:=ADR(Str); (\* Variable address \*)
SNMPMng.Address:=ADR('192.168.0.184'); (\* Agent address \*)
SNMPMng.OID:=ADR('1.3.6.1.4.1.36955.2'); (\* OID \*)
END_IF;
(\* SNMP manager. \*)
SNMPMng.Enable:=Di00CPU;
SNMPMng(); (\* SNMP manager \*)
(\* Check if the answer from Agent has been received and manage it. \*)
IF (SNMPMng.Ok) THEN
Ok:=TO_BOOL(SysStrFind(ADR(Str), ADR('Hello!'), FIND_DEFAULT) = ADR(Str));
(\* [End of file] \*)