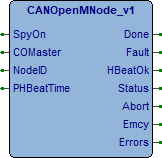
Questo blocco funzione gestisce un modulo CAN su di una rete CANOpen gestita dal FB CANOpenMaster, occorre passare al FB l’indirizzo di allocazione del FB CANOpenMaster a cui è connesso il modulo. Il FB gestisce la ricezione e l’invio dei messaggi CANOpen da e verso il nodo.
Upgrade list
- Se l’oggetto aggiornato non è nell’ultima versione del package, vedi capitolo “Aggiornamento librerie” in questo articolo.
- Gli oggetti obsoleti sono inseriti nella libreria eLLabObsoleteLib fare riferimento al relativo manuale ed al manuale programmazione in formato pdf.
CANOpenMNode
Gestiva soltanto lettura/scrittura SDO, mentre il nuovo modulo (Object oriented) ha una serie di metodi per gestire il PDO mapping. Eliminata la definizione “CANOMMCTYPE” ora si utilizza la chiamata ai metodi relativi.
Descrizione
SpyOn (BOOL) Se attivo permette di spiare il funzionamento della FB.
COMaster (@CANOpenMaster_v1) Indirizzo FB CANOpenMaster di gestione protocollo.
NodeID (BYTE) Definizione ID nodo da gestire.
PHBeatTime (UINT) Definizione tempo invio heartbeat (mS) (Vedi Meccanismo Heartbeat).
Done (BOOL) Attivo per un loop al termine esecuzione comando.
Fault (BOOL) Attivo per un loop se errore esecuzione. Può verificarsi su heartbeat o in caso di errore nei dati in ricezione.
HBeatOk (BOOL) Attivo se definito tempo di invio heartbeat e se il dispositivo lo invia.
Status (CO_NMT_STS) Stato del modulo (Definizione).
Abort (CO_ABORT) Struttura dati ricezione codice di abort dal modulo (Definizione).
Emcy (CO_EMERGENCY) Struttura dati ricezione codice di emergenza dal modulo (Definizione).
Errors (UDINT) Counter errori gestione modulo.
Meccanismo Heartbeat
Sul nodo slave è possibile gestire anche contemporaneamente 2 diversi meccnismi di heartbeat:
Producer heartbeat
Generato dal nodo e controllato dalla FB CANOpenMNode. Impostando un tempo nel parametro PHBeatTime (Producer Heartbeat Time, in millisecondi) il nodo viene configurato per inviare ogni tempo definito un messaggio Heartbeat (Registro 1017h Producer Heartbeat Time). Il FB controlla la ricezione del messaggio ed attiva l’uscita HBeatOk. Se ogni tempo impostato +50mS non viene ricevuto il messaggio dal nodo si disattiva l’uscita.
Consumer heartbeat
Generato dalla FB CANOpenMaster e controllato dal nodo. Impostando un tempo nel parametro CANOpenMaster.PHBeatTime (Producer Heartbeat Time, in millisecondi), il nodo viene configurato per controllare la ricezione del messaggio dal nodo master (Registro 1016h Consumer Heartbeat Time). Se ogni tempo impostato +50mS non viene ricevuto il messaggio il nodo slave và in errore, il comportamento in caso di errore può essere configurato.
Metodi disponibili
Reset
Questo metodo esegue il reset del nodo can slave ponendolo in condizione di inizializzazione.
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.

Start
Questo metodo forza in operational il nodo can slave.
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.

SDORead
Questo metodo esegue la lettura di un oggetto SDO (Service Data Objects).
OIndex (UINT) Indice Object dictionary.
OSIndex (USINT) Sottoindice Object dictionary.
OType (VR_TYPE) Tipo variabile letta da Object dictionary.
OAddress (PVOID) Indirizzo variabile appoggio valore letto.
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.

SDOWrite
Questo metodo esegue la scrittura di una variabile in un oggetto SDO (Service Data Objects).
OIndex (UINT) Indice Object dictionary.
OSIndex (USINT) Sottoindice Object dictionary.
OType (VR_TYPE) Tipo variabile da scrivere in Object dictionary.
OAddress (PVOID) Indirizzo variabile da scrivere.
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.

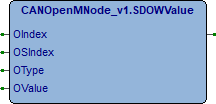
SDOWValue
Questo metodo esegue la scrittura di un valore in un oggetto SDO (Service Data Objects).
OIndex (UINT) Indice Object dictionary.
OSIndex (USINT) Sottoindice Object dictionary.
OType (VR_TYPE) Tipo valore da scrivere in Object dictionary.
OValue (DWORD) Valore da scrivere.
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.
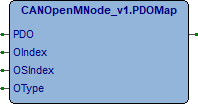
PDOMap
Questo metodo esegue mappatura di un oggetto in un PDO (Process Data Object). Più oggetti possono essere mappati all’interno di un PDO, occorre fare riferimento alla dimensione di ogni oggetto per non superare 8 bytes.
PDO (STRING[6]) Definizione PDO (Esempio RPDO1, TPDO4, …).
OIndex (UINT) Indice oggetto.
OSIndex (USINT) Sottoindice oggetto.
OType (VR_TYPE) Tipo oggetto.
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.
PDOUMap
Questo metodo esegue la smappatura di un PDO (Process Data Object).
PDO (STRING[6]) Definizione PDO (Esempio RPDO1, TPDO4, …).
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.

PDOCom
Questo metodo esegue le impostazioni della comunicazione di un PDO (Process Data Object).
PDO (STRING[6]) Definizione PDO (Esempio RPDO1, TPDO4, …).
COBID (WORD) COB assegnato al PDO.
TType (USINT) Tipo trasmissione.
ITime (UINT) Tempo di inhibit, impostabile sui TPDO, espresso in multipli di 100 μs. Ritardo minimo trasmissione TPDO per non sovraccaricare il bus su eventi in rapida successione. Impostabile solo se TType 254 o 255 (0 disabilita).
Il metodo ritorna (BOOL), FALSE se comando in corso, TRUE comando eseguito.

| TType | Descrizione |
|---|---|
| 0 | Synchronous (acyclic) |
| 1~240 | Synchronous (cyclic every (1~240)-th sync) |
| 241~253 | Not used |
| 254 | Event-driven (manufacturer-specific) |
| 255 | Event-driven (device profile and application profile specific) |
Esempi
PDOCom('TPDO1', 16#180+NodeID, 255, 100); //Event-driven, 10mS inhibit time
PDOCom('TPDO1', 16#180+NodeID, 1, 0); //Synchronous every SYNC
PDOCom('RPDO1', 16#200+NodeID, 1, 0); //Synchronous every SYNC
PDOCom('RPDO1', 16#200+NodeID, 10, 0); //Synchronous every 10th SYNCDizionario oggetti
Il dizionario degli oggetti (Object Dictionary) è l’insieme degli oggetti utilizzati per configurare, inviare comandi e monitorare grandezze in CANOpen.
Elenco oggetti
- 16#0000 not used
- 16#0001-16#001F Static Data Types
- 16#0020-16#003F Complex Data Types
- 16#0040-16#005F Manufacturer Specific Complex Data Types
- 16#0060-16#007F Device Profile Specific Static Data Types
- 16#0080-16#009F Device Profile Specific Complex Data Types
- 16#00A0-16#0FFF Reserved for further use
- 16#1000-16#1FFF Communication Profile Area
- 16#2000-16#5FFF Manufacturer Specific Profile Area
- 16#6000-16#9FFF Standardised Device Profile Area
- 16#A000-16#BFFF Standardised Interface Profile Area
- 16#C000-16#FFFF Reserved for further use
Oggetti standardizzati
Ogni dispositivo CAN ha un proprio dizionario di oggetti ed occorre consultare la documentazione relativa per un elenco (File EDS). Esistono comunque oggetti che sono presenti in molti dispositivi eccone un elenco.
| Index | Sub | Type | Access | Description |
| 16#1000 | 0 | UDINT | R | Device type: Tipo dispositivo |
| 16#100C | 0 | UINT | R/W | Guard time (mS): Moltiplicato per Live time factor fornisce la durata per il Lifeguarding t (0 disabilita). |
| 16#100D | 0 | USINT | R/W | Live time factor |
| 16#1017 | 0 | UINT | R/W | Producer heartbeat time (mS): Tempo di invio messaggio heartbeat (0 disabilita). Heartbeat disabilita il Nodeguarding. |
| 16#1029 | 1 | USINT | R/W | Error behaviour: Definisce lo stato del dispositivo in caso di errore. 0:Preoperational, 1:No change, 2:Stopped |
| 16#1400~FF | R/W | Receive PDO communication parameter: Mappatura oggetti RPDO. | ||
| 16#1600~FF | R/W | Receive PDO mapping parameter: Mappatura comunicazione RPDO. | ||
| 16#1800~FF | R/W | Transmit PDO communication parameter: Mappatura comunicazione TPDO. | ||
| 16#1A00~FF | R/W | Transmit PDO mapping parameter: Mappatura oggetti TPDO. |
Spionaggio comunicazione
Se SpyOn attivo è possibile utilizzare utilizzare la console di spionaggio per verificare il funzionamento della FB. Per la definizione dei livelli di trigger e per il formato del record di spionaggio si rimanda alla CANOpenMaster.
Considerazioni
Esempi
Come utilizzare gli esempi.
Riportiamo due blocchi funzioni per la gestione di moduli di I/O Can open, i FB sono da utilizzarsi insieme al FB CANOpenMaster. Vedere programma ST_CANOpenMaster per il loro utilizzo.
Il FB iRCop esegue la gestione del modulo comunicazione I/O Remoti CANOpen serie iR della Weintek. Nel FB sono gestiti 8 ingressi e 8 uscite ma può essere modificato per adattarlo alle proprie esigenze.
LogicLab (Ptp184, (FB) CanDOut)
FUNCTION_BLOCK CanDOut
VAR
CaseNr : UINT; (* Case programma *)
TPDOData : ARRAY[0..1, 0..7] OF BYTE; (* TPO data, Rx Tx *)
MNode : CANOpenMNode_v1; (* CANOpen master node *)
END_VAR
VAR_INPUT
SpyOn : BOOL; (* Spy active *)
NodeID : BYTE; (* Node address *)
Output : BYTE; (* Outputs to module *)
COMaster : @CANOpenMaster_v1; (* CANOpen master *)
PHBeatTime : UINT; (* Producer Heartbeat Time (mS) *)
END_VAR
VAR_OUTPUT
HBeatOk : BOOL; (* Heartbeat Ok *)
DType : DWORD; (* Device type *)
Abort : CO_ABORT; (* Abort received *)
Emcy : CO_EMERGENCY; (* EMCY service *)
Errors : UDINT; (* Error counter *)
END_VAR
// *****************************************************************************
// FUNCTION BLOCK "CanDOut"
// *****************************************************************************
// Manages a 8 digital outputs module.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// MANAGE CAN OPEN NODE
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Initialize the node parameters.
MNode.SpyOn:=SpyOn; //Spy active
MNode.NodeID:=NodeID; //Node address
MNode.PHBeatTime:=PHBeatTime; //Producer Heartbeat Time (mS)
// If master is defined manages the node, on error initializes the module.
IF (COMaster = eNULL) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
MNode(COMaster:=COMaster); //CANOpen master node
HBeatOk:=MNode.HBeatOk; //Heartbeat Ok
// =========================================================================
// CHECK DIAGNOSTIC
// =========================================================================
// The abort and emergency status are copied out.
IF (MNode.Abort.Recd) THEN Abort:=MNode.Abort; END_IF;
IF (MNode.Emcy.Recd) THEN Emcy:=MNode.Emcy; END_IF;
// =========================================================================
// PREOPERATIONAL STATE
// =========================================================================
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// MODULE COMMANDS
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Execute the mdule commands.
CASE (CaseNr) OF
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// MODULE STARTUP
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Reset the module.
0: IF (MNode.Reset()) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Reads the device type (it's just to show).
1: IF (MNode.SDORead(16#1000, 0, DWORD_TYPE, ADR(DType))) THEN CaseNr:=100; END_IF;
// ----------------------------------------------------[Mapping RPDO1]--
// +----------+-[1 BYTE]-+-----+-----+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
// | 0x200+ID | Outputs | |
// +----------+----------+-----+-----+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
// Map "Write output 001h to 008h" (Index 16#6200, SubIndex=1, 1 BYTE).
// Set communication register, COB-ID=16#200+NodeID.
100: IF (MNode.PDOMap('RPDO1', 16#6200, 1, BYTE_TYPE)) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
101: IF (MNode.PDOCom('RPDO1', 16#200+NodeID, 16#FF, 100)) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
102: CaseNr:=200;
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Start module.
200: IF (MNode.Start()) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
201: IF (MNode.Status <> CO_NMT_STS#OPERATIONAL) THEN CaseNr:=0; END_IF;
END_CASE;
// =========================================================================
// OPERATIONAL STATE
// =========================================================================
// If module is not operational the PDO are not managed.
IF (MNode.Status <> CO_NMT_STS#OPERATIONAL) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// LOGIC I/O MANAGEMENT
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// On output status change send it to the RPDO1.
IF (SysIsCANRxTxAv(TRUE) AND (Output <> TPDOData[1, 0])) THEN
TPDOData[1, 0]:=Output; //TPO data, Rx Tx
eTO_JUNK(@COMaster.RPDOTx(16#200+NodeID, ADR(TPDOData[1, 0]), 1));
END_IF;
// [End of file]LogicLab (Ptp184, (FB) iRCop)
FUNCTION_BLOCK iRCop
VAR
CaseNr : UINT; (* Case programma *)
TPDOData : ARRAY[0..1, 0..7] OF BYTE; (* TPO data, Rx Tx *)
MNode : CANOpenMNode_v1; (* CANOpen master node *)
END_VAR
VAR_INPUT
SpyOn : BOOL; (* Spy active *)
NodeID : BYTE; (* Node address *)
COMaster : @CANOpenMaster_v1; (* CANOpen master *)
PHBeatTime : UINT; (* Producer Heartbeat Time (mS) *)
Output : BYTE; (* Outputs to module *)
END_VAR
VAR_OUTPUT
HBeatOk : BOOL; (* Heartbeat Ok *)
DType : DWORD; (* Device type *)
Input : BYTE; (* Inputs from module *)
Abort : CO_ABORT; (* Abort received *)
Emcy : CO_EMERGENCY; (* EMCY service *)
Errors : UDINT; (* Error counter *)
END_VAR
// *****************************************************************************
// FUNCTION BLOCK "iRCop"
// *****************************************************************************
// Manages the Weintek iRCop I/O module.
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// MANAGE CAN OPEN NODE
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Initialize the node parameters.
MNode.SpyOn:=SpyOn; //Spy active
MNode.NodeID:=NodeID; //Node address
MNode.PHBeatTime:=PHBeatTime; //Producer Heartbeat Time (mS)
// If master is defined manages the node.
IF (COMaster = eNULL) THEN RETURN; END_IF;
MNode(COMaster:=COMaster); //CANOpen master node
HBeatOk:=MNode.HBeatOk; //Heartbeat Ok
// =========================================================================
// CHECK DIAGNOSTIC
// =========================================================================
// The abort and emergency status are copied out.
IF (MNode.Abort.Recd) THEN Abort:=MNode.Abort; END_IF;
IF (MNode.Emcy.Recd) THEN Emcy:=MNode.Emcy; END_IF;
// =========================================================================
// PREOPERATIONAL STATE
// =========================================================================
// Execute the module commands.
CASE (CaseNr) OF
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// MODULE STARTUP
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Reset the module.
0: IF (MNode.Reset()) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Reads the device type (it's just to show).
1: IF (MNode.SDORead(16#1000, 0, DWORD_TYPE, ADR(DType))) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
// Set the error behavior on heartbeat error.
// Index 1029-01: Module goes on Pre-operational
// Index 6206-01: Digital outputs (01h to 08h) output value are given in 6207
// Index 6207-01: Digital outputs (01h to 08h) set to FALSE
2: IF (MNode.SDOWValue(16#1029, 1, BYTE_TYPE, 2)) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
3: IF (MNode.SDOWValue(16#6206, 1, BYTE_TYPE, 16#FF)) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
4: IF (MNode.SDOWValue(16#6207, 1, BYTE_TYPE, 16#00)) THEN CaseNr:=100; END_IF;
// --------------------------------------------------[Mappatura TPDO1]--
// +----------+-[1 BYTE]-+-----+-----+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
// | 0x180+ID | Inputs | |
// +----------+----------+-----+-----+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
// Map "Read input 001h to 008h" (Index 16#6000, SubIndex=1, 1 BYTE).
// Set communication register, COB-ID=16#180+NodeID.
100: IF (MNode.PDOMap('TPDO1', 16#6000, 1, BYTE_TYPE)) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
101: IF (MNode.PDOCom('TPDO1', 16#180+NodeID, 16#FF, 100)) THEN CaseNr:=110; END_IF;
// --------------------------------------------------[Mappatura RPDO1]--
// +----------+-[1 BYTE]-+-----+-----+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
// | 0x200+ID | Inputs | |
// +----------+----------+-----+-----+----+-----+-----+-----+-----+
// Map "Write output 001h to 008h" (Index 16#6200, SubIndex=1, 1 BYTE).
// Set communication register, COB-ID=16#200+NodeID.
110: IF (MNode.PDOMap('RPDO1', 16#6200, 1, BYTE_TYPE)) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
111: IF (MNode.PDOCom('RPDO1', 16#200+NodeID, 16#FF, 100)) THEN CaseNr:=200; END_IF;
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------
// Start module.
200: IF (MNode.Start()) THEN CaseNr:=CaseNr+1; END_IF;
201: IF (MNode.Status <> CO_NMT_STS#OPERATIONAL) THEN CaseNr:=0; END_IF;
END_CASE;
// =========================================================================
// OPERATIONAL STATE
// =========================================================================
// If module is not operational the PDOs are not managed.
IF (MNode.Status <> CO_NMT_STS#OPERATIONAL) THEN Input:=16#00; RETURN; END_IF;
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// LOGIC I/O MANAGEMENT
// -------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Return the logic inputs status from TPDO1, waited only 1 byte.
IF (@COMaster.TPDORx(16#180+NodeID, ADR(TPDOData[0, 0])) <> 0) THEN
Input:=TPDOData[0, 0]; //Inputs from module
END_IF;
// On output status change send it to the RPDO1.
IF (SysIsCANRxTxAv(TRUE) AND (Output <> TPDOData[1, 0])) THEN
TPDOData[1, 0]:=Output; //TPO data, Rx Tx
eTO_JUNK(@COMaster.RPDOTx(16#200+NodeID, ADR(TPDOData[1, 0]), 1));
END_IF;
// [End of file]